Blog Archives
Detection of Sumatra forest fire and air pollution index using remote sensing satellites
During this week, news reported that forest fires happen at Sumatra, Indonesia which cause dangerous haze (API more than 300) at Singapore and some part of Johor, Malaysia.
By using remote sensing (RS) satellites, important atmospheric and land parameters such as LST (land surface temperature), wind direction, and aerosol optical thickness / air pollution index (API) can be retrieved to determine:
1. Location of forest fires
2. Direction of smoke
3. The hazardous level of haze .
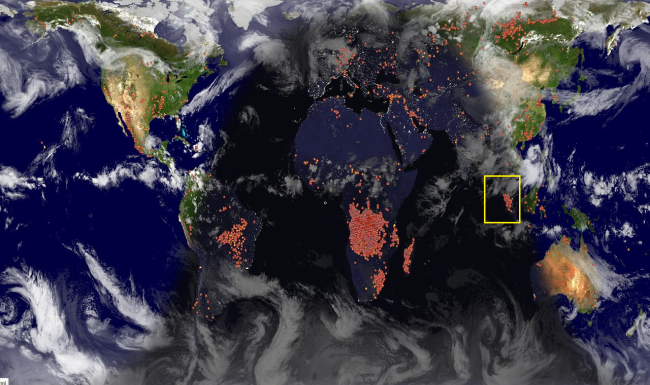
Location of forest fires. (Source)
Near real time/ real time data of global forest fires are freely available at:
(http://satellite.ehabich.info/globalfire.htm)
Image above retrieved on 20 June 2013 22:35 GMT show many hot spots at Sumatra, Indonesia (yellow box). This image produced using NASA EOS MODIS satellite.
Hazardous level of haze
Real time air pollution index (API) is freely available at http://aqicn.org/?map .
Different countries using different scale on how to describe the risky level of API. For Malaysia, the scale is given by:
From the image of API above (retrieved on 21 June 2013), Muar and Pasir Gudang are both within Johor reported more than 300 API (Very unhealthy). According to news report, Malaysia government already closed down schools at the haze affected areas. By history, the highest API value ever recorded was 839 in Kuching on 23 September 1997 during the 1997 Southeast Asian Haze.